Latest Research
- 2016.08.01
- Osakada Group
Synthesis the polymers composed of Si-containing aromatic rings and their properties by ,σ.π-conjugation of the polymer chain
Polymers composed of Si-Si bond in the main chain, are much less common than the carbon polymers, but they are expected to exhibit unique properties, such as photoconductivity, derived from the rigid polymer chain as well as its σ,π-conjugation, and are regarded as the compounds for new materials. Dehydrogenative polycondensation of organosilanes (R2SiH2, RR'SiH2, RSiH3 etc) catalyzed by transition metal complexes is a clean synthesis of the polysilanes. The conventional Ti catalysts, however, showed low activity for the polycondensation of the secondary organosilanes. Thus, development of a new synthetic catalysis for the reaction has been expected.
We have investigated polycondensation of the organosilanes catalyzed by Ni complexes, and succeeded in formation of the polysilanes with new structures, novel type of the regulation of molecular weights, and new insight of the synthetic reactions.
1) Polysilane formation via a cyclic intermediate.
Dehydrogenative polycondensation of secondary oraganosilanes produces cyclic and linear polysilanes, while optimization of the conditions results in formation of either of the polymers. Careful study of the reaction mixture, in addition to the isolation of model compounds containing Pt center, revealed that the following reactions promote the growth of the polysilanes. Cyclic oligosilanickel intermediate is formed at first, and then addition of a monomer and its insertion into the Ni-Si bond of the cyclic or acyclic intermediates. Repetition of the reactions affords the polysilanes.
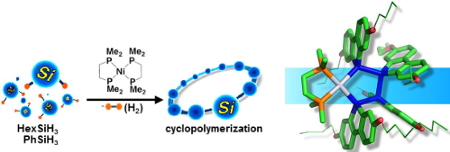
Figure 1. Formation of cyclic polysilanes and metallacycle as the
polycndensation intermediate.
The above results are closely related to the formation of a single activated species in the catalysis, which enhances the polymer growth with high selectivity.1)
2) Polycondensation of silafluorenes and the product: polymer composed of main chain with σ-conjugation and side chain contributing to π-conjugation.
Polymer of silafluorene, a π-conjugated molecule, is expected to have the electric-conductive properties and related functions, although low reactivity of the compound and low solubility of the produced polymer prevented detailed investigation. We adopted alkyl-substituted monomer and the nickel complex catalyst, and obtained the Si-polymers with clear molecular structures and regulated molecular weights. The tetramer, obtained from a separate route, was characterized by X-ray crystallography, which indicated close and parallel contact, and interaction of the π-electrons between the aromatic planes. Comparison of the absorption and fluorescence spectra of the monomer, tetramer, and the polymer revealed that the polymer has the π-stacked structure shown in Figure 2.2)
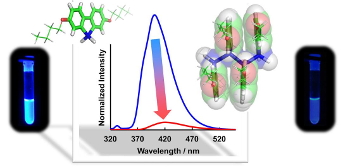
Figure 2 π-Stacking of tetramer of silafluorene and the optical
properties
3) New molecular weight control in the polycondensation
We further investigated the polycondensation of silafluorene using the nickel catalysts, and revealed the mechanism for the molecular weight control in it. Polymerization in an open system stops the polymer growth due to consumption of the monomer, but it resumes the reaction in the presence of a small amount of dihydrogen in the closed reaction system.
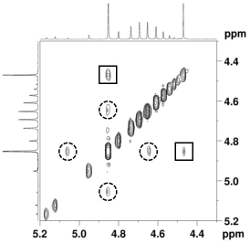
Figure 3 EXSY-NMR spectrum of the reaction mixture and exchange
of the hydrogen of the monomer and the oligomer
As shown in Figure 3, the EXSY-NMR spectrum of the reaction mixture indicated mutual exchange of the hydrogens between the monomers and between the monomer and an oligomer. Based on it, we concluded that the catalysis generates a sole active species and it enhances the bond formation between the monomer and an oligomer rather than that between the oligomers.3)
In addition to reversibility of the reaction, all the results indicate the reaction mechanism that serves to regulate the molecular weights. Figure 4 shows the polymerization, leading to the molecular weight control of the products, is classified into four categories. The present polymerization is a new type of polycondensaiton reaction because it forms a new Si-Si bond between the monomer and the oligomer, and the metal center is once detached from the growing polymer after the reaction.4)
Unique character of the reaction as well as functions of the polymers utilizing the polymer structures are now in progress. Dithienosilole with a similar structure to silafluorene has been recently found to undergo new migration reaction in the presence of Ni and Pt catalyst, which are a new target of this study.5)
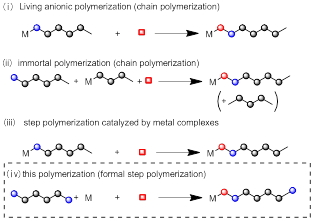
Figure 4 Molecular weight control of the polymerization including
this study.
1) M. Tanabe, A. Takahashi, T. Fukuta, K. Osakada, Organometallics,
2013, 32, 1037-1043.
2) M. Tanabe, S. Iwase, A. Takahashi, K. Osakada, Chem. Lett.,
2016, 45, 394-396.
3) M. Tanabe, S. Iwase, A. Takahashi, K. Osakada, in press.
4) Living radical polymerization using special reagents is also
categorized in it.
5) Manuscript in preparation.



